Advanced solution in Thermodynamics

The Thermodynamic Database and Applications
|
Advanced solution in Thermodynamics |
|
 |
|
|
The Thermodynamic Database and Applications |
Project Concept and Process Analysis
Documentation of the MS Excel File
CuFeS2.xls
Download and save the both files in same folder:
CuFeS2.xls and
TurbulentFurnace.jpg
Open the file CuFeS2.xls with Microsoft Excel Application
Download the AsTher
Applications
Execute the Application AsTher\bin\XProCalc.exe
Excel Sheet [frn]: Process Definition
| A | B | C | D | |
| 1 | eql | [A1]=eql | ||
| 2 | T [C] | 1250 | ||
| 3 | P [bar] | 1 | ||
| 4 | Phases | gas | [B4] . . .[G4] Name of the Excel Worksheet, in which the phases are defined (more information) | |
| 5 | Calculation Conditions | (more information) | ||
| 6 | Count | 0 | 50 | Number in [B1] is increased by +1 after each calculation (more information) |
| 7 | Precision | 0.001 | Precision of the thermodynamic calculation | |
| 8 | Iterations Steps | 98000 | Maximum iterations Steps of the thermodynamic calculation | |
| 9 | Visualisation | Visual | Name of the Excel-Sheet for visual representation | |
| 10 | Following Calculation | * | [B10] Name of the Excel file, [B11] Excel Sheet of the following calculation, *: in [B10] or [B11] means the same Excel file or same sheet as the current calculation | |
| 11 | Recorder | rec | Name of the Excel Worksheet into which the application writes the data specified below (more information) | |
| 12 | T [C] | =B2 | Linked or given data to write in the Recorder Sheet | |
| 13 | Air [Nm³] | =B6*10 | Variable for the current calculation | |
| 14 | O2 [kg] | =gas!B13 | ||
| 15 | CuFeS2 (s) [kg] | =sol!B2 | ||
| 16 | Slag [kg] | =slg!C13 | ||
| . | dH | =gas!L17+slg!L13+mat!L8+sol!L6 | ||
| . | Ca2SiO4 (l) | =slg!C2 | ||
| . | CaO (l) | =slg!C3 | ||
| . | CaSO4 (l) | =slg!C4 | ||
| . | CuFe2O4 (l) | =slg!C6 | ||
| . | CuFeO2 (l) | =slg!C7 | ||
| . | Fe0.947O (l) | =slg!C8 | ||
| . | Fe3O4 (l) | =slg!C10 | ||
| . | FeO (l) | =slg!C11 | ||
| . | Fe2SiO4 (l) | =slg!C9 | ||
| . | SiO2 (l) | =slg!C12 | ||
| . | Fe (l) | =mat!C6 | ||
| . | Cu (l) {matte} | =mat!C2 | ||
| . | Cu2S (l) {matte} | =mat!C3 | ||
| . | FeS (l) {matte} | =mat!C5 | ||
| . | Cu2O (l){slag} | =slg!C5 | ||
| . | matte [kg] | =mat!C8 |
MS Excel Sheets for phases
(gas phase[gas], slag [slg], matte [mat] and solid [sol])
The data in the cells with green background colour is entered, calculated or written
by users.
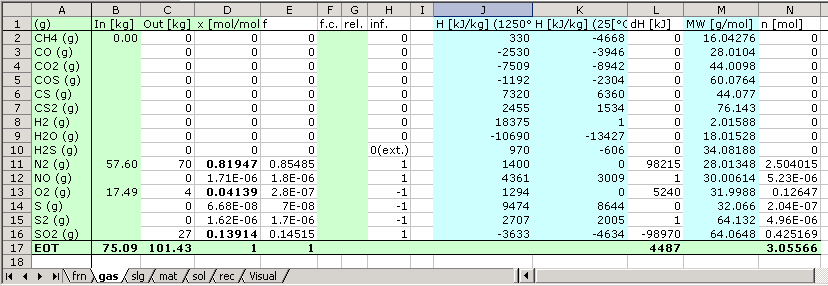
Cell [A1]: Aggregate state of the phase, (g),(l) or (s)
Cells [B1],[C1]: Dimension of the input and output values e.g.:
[kg], [mol], [lb], [Nm³]. . .
Cells [B1] to [B16]: contains input values. The input data can be a link to another file or cell. The data can also be entered into phase tables.
Column [I], [J], [M]: Users can cause the application to write the values of the state functions or properties of the substances
Column [L], [N]: individual calculation of a user based on state functions or physical data.
If cells [I1] or [J1] contain a state function such as Cp, H, G, S, the application writes the values of the state functions during each calculation according to the given temperature.
MS Excel Sheets for data record [rec]
The table data is written by the process calculator XProCalc.exe.
corresponding tot he given parameter in the sheet [frn]
The graphics are defined by the user.
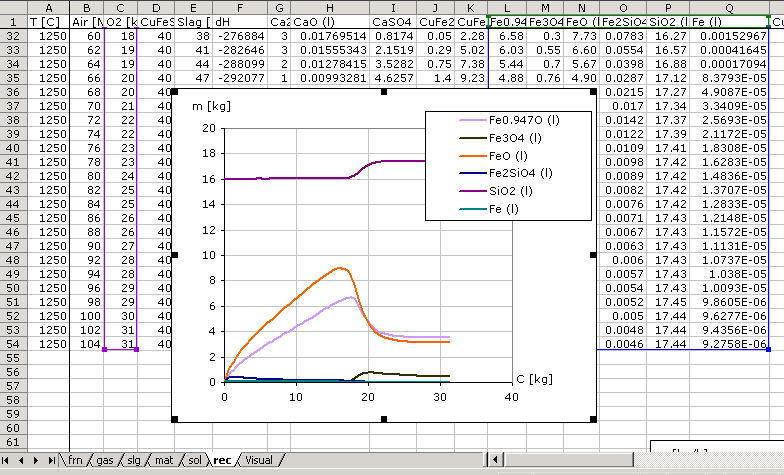
Visual display of the calculations results, MS Excel Sheets for Visual Window [rec]
|
The following figure shows how to enter links to the calculation results. Entering links and data format is a matter of users. 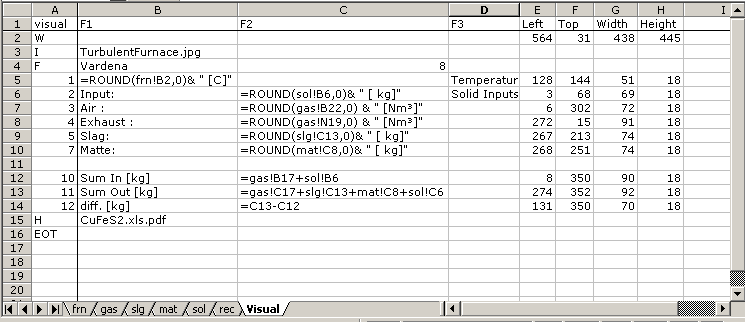 |
Visual
Window of Process Calculator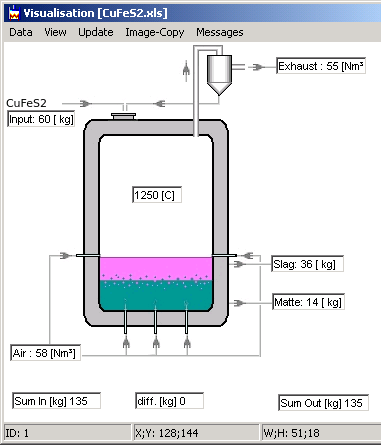 |