1. Database Administration
Content
1.1. Database-Window definition of a new
dataset
1.2. Correlation-Window creation
datasets
using the values of the state
function
1.3. Reaction-Data-Window:
calculation the values of the state
function using equilibrium data of
reactions
1.4. Graphic-Window display the datasets
in Database, Correlation and
Reaction Windows
The application allows to create and to change thermodynamic datasets
1.1.
Database-Window
1.1.1. General Information
1.1.2. Important menu functions
Menu Database
Database -> New: creates a new data source
Database -> Open: opens an existing database
Database -> Add: adds an another database to the current database.
No check for redundancy of datasets will be made!
Database -> Close: closes the active database file.
Menu Dataset
Dataset -> Select by double click:
When it is checked, the data sets can be selected
only by mouse double click or by enter-key on keyboard.
When it is not checked, the data sets can be selected by simple
mouse
click or arrow-keys on keyboard
You can select data sets
by navigations buttons.
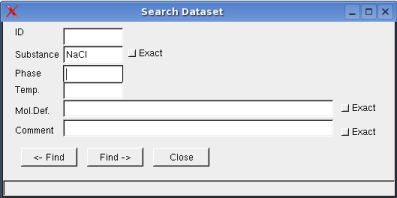
Dataset -> Search: opens a dialog box to search the dataset for
given criteria
When the checkbox exact is not activated, data items
of string format will be listed according to next match of the
respective character sequence.
The temperature range relates to the
validity of the data.
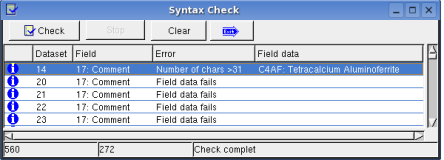
Dataset -> Syntax Check:
Dataset -> Sort: sorts dataset alphabetic.
Dataset -> Renew Index: The ID of the datasets will be changed
in ascending order
Information
Information -> Messages: shows the Message Window
Information -> Help: shows this text in browser, which is given in AsTher.sys
1.2.
Correlation-Window
1.2.1. General Information
A new thermodynamic dataset can be created using single data of state
functions,
when Cp-, H-, S-, or G- values at different temperatures are known.
Enter the known data into the respective columns.
If datasets for gases are to create according to real gas
rules, "(g)" must be written in the field "Phase" and Tc and Pc must be
known.
The correlation can be calculated using Cp, H and/or G values.
The corresponding Check Boxes must be checked (active).
The temperature must always known.
One or more values of Cp, H, S, G must be given in the
Correlation-Dataset.
When H, S or G are included, the reference values T0, H0, S0 must
be given.
The Cp Function is defined by:
Cp= a + b . 0.001 .
T
+ c . 106 . T -2
+ d . 10 -6 . T2 + e .
109 . T -3 + f . 10 -9
. T3
or
Cp= a + b . (T/1000)
+ c . (T/1000) -2
+ d . (T/1000)2 + e .
(T/1000) -3 + f . (T/1000)3
According to the selection in the example above, the correlation will
calculate only the coefficients a, b, c, and d . These selections
should be changed until a sufficiently high correlations-coefficient is
reached. This coefficient ranges from 0 to 1; 0
: no relation; 1: best correlation . A
comparison of given and calculated values in the valid temperature range should serve as
double check.
Many data sources list values for enthalpy, entropy and
free energy according to the law of ideal gas. If these data are taken,
only the Cp-values should be correlated in order to create a complete
dataset for real gas behaviour.
In AsTher, the standard state is defined
at 1 bar and 298.15 K, i.e.: enthalpy of a pure substance at this state
is zero.
If data related to a different standard definition are taken for
the correlation the results will not be compatible with datasets of
AsTher.
You can transfer the Correlation-Dataset to the Database-Dataset.
When "All" checked, the data will be replaced in the table
Database-Dataset, even if a fields in the Correlation-Dataset does not
contain any entry.
When "All" not checked, the fields will not replaced data in the
Database-Dataset, when the corresponding filed in Correlation-Dataset
contains no any data (blank).
1.3.
Reaction-Data-Window - Calculation of the State Functions
1.3.1. General Information
If the equilibrium constant of a reaction is known, the H, S and G
values of a substance can be determined corresponding to
the Van' t Hoff – relations
When the state function calculated in this window, the data can be
transferred to the correlation-window and
the dataset can be created.
In this window, the equilibrium constant
will be linearly correlated vs. temperature on the basis of the entered
data on page K(T). The
correlation can be conducted either totally or differentially. In case
of smaller temperature ranges, the correlation should be carried out
totally. With wider temperature ranges, a total correlation can produce
erroneous results. As results from the correlation K and ΔH will be
calculated and displayed on page K(T)Int. Based on those values for K
and H, S and G are calculated and displayed on page dH,dS,dG and
likewise H, S, G on
page H,S,G. If the
differential values for dH,dS,dG are known for a reaction, those can be
entered on the respective page. In this case, the inputs on page Kf(T)
will not be considered and
there will be no value displayed on page K(T)Int. If the calculation is
conducted successfully, the data for H, S, G can be transferred to the
correlation table together with the temperature values. Press button
replace to replace the data in the correlation table by those values.
If the dialog box is closed by Button add, the calculated values will
be added to the correlation table without replacing the existing data.
1.3.2. Example
In following, the data are entered in the Sheet Kf(T)
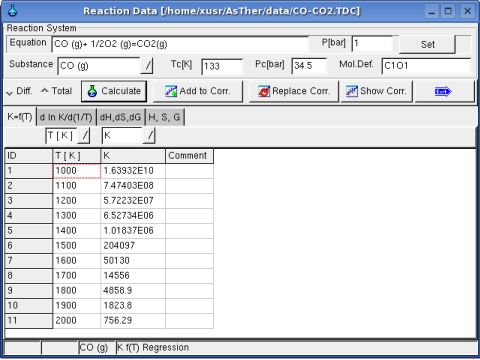
Regression option is for differential or total correlation selected,
and the button Calculate pressed.
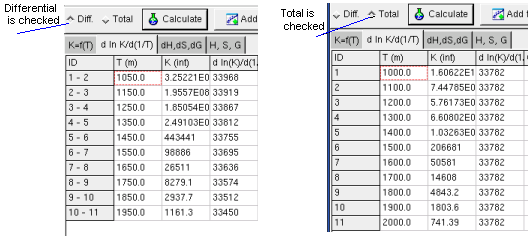
The Sheet dH, dS, dG shows calculated change of the
state functions by reaction, when the K and T values given in the first
sheet (Kf(T)).
When K and T values are unknown, but the several values of dH and/or
dS and/or dG are known,
these values can be are entered in the the Sheet dH, dS, dG.
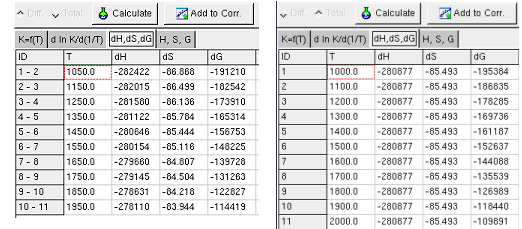
When the button calculate is pressed and the Sheet dH,
dS, dG is shown, the calculation carried out only with the
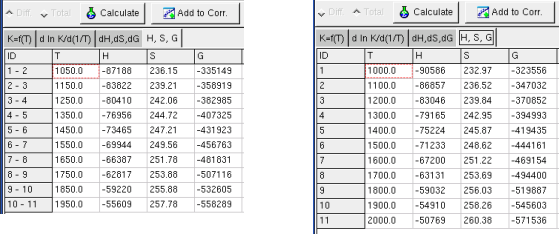
data in this sheet. The values of the state function are shown in the
Sheet H, S, G .
In the Sheet dH, dS, dG, not all values of
ΔH,
ΔS and
ΔG of a reaction have to be entered.
When
ΔH,
ΔS entered without
ΔG , the application calculates
ΔG corresponding
ΔG =
ΔH-ΔS.
When
ΔS,
ΔG entered without
ΔH , the application calculates
ΔH corresponding
ΔG =
ΔH-ΔS.
When only one of
ΔH or
ΔS or
ΔG is entered, the application calculate only corresponding H or S
or G,
1.4.
Graphic-Window
1.4.1. General Information
Δ










